'An estimated 1.100 million young people are at risk of hearing loss'
Noise hearing loss is spreading more intensely among youth in recent years. Teresa Rivera Rodríguez, professor at the University of Alcalá and Head of the Otolaryngology Service at the Príncipe de Asturias University Hospital in Alcalá de Henares.
In this interview, Teresa comments for uah.esnoticia on the keys to this problem and talks about how to prevent injury, since hearing loss is not reversible.
- What has happened to hearing problems in young people in recent years?
Hearing loss (hearing loss or deafness) in young people may be due to multiple causes, either genetic or environmental, such as medication administration, infections or noise exposure. Of these, the most frequent is that produced by exposure to noise, either by frequent venues with poor acoustics and intense noise, or in the work environment, or even the domestic one when hearing the music very loud.
Noise above 85 decibels is considered harmful to hearing. In recent years, noise-induced hearing loss has been on the rise, according to the World Health Organization, an estimated 1.100 million young people, aged 12 to 35, are at risk of hearing loss from their exposure to noise in recreational contexts.
- Types of hearing loss in young people. What factors in the environment are involved in this process?
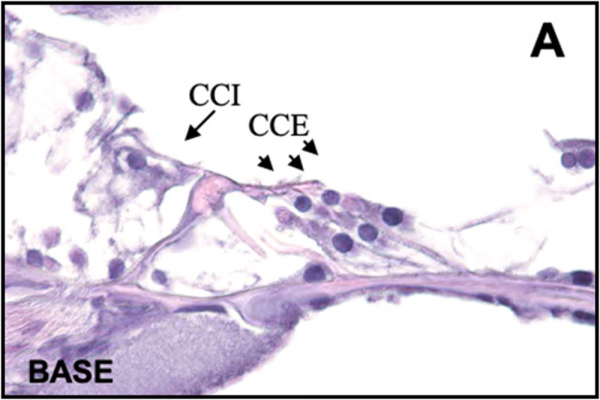
The most common hearing loss in young people, which as I have already mentioned is noise, is a neurosensory hearing loss, that is, that affects the inner ear. There is injury to the outer hair cells and subsequently the inner hair cells, these lesions being irreversible.
In Figure A, we can see a histological representation showing outer hair cells and the inner hair cels with normal characteristics. However, in Figure B we can see these cells injured by exposure to noise. These lesions are similar to other causes that produce sensorineural deafness, such as the administration of orthotoxic drugs.

Figure B. Outer and inner hair cells injured by noise exposure
- Noise in public premises VS noise in workplaces, Do you know which of both issues is causing in young people? If a young person is exposed to excessive noise in both his or her work environment and in his or her free time, how will he be affected?
Noise in both public premises and workplaces can affect hearing in young people, although it is the most common in young people under the age of 30 in the first case.
The hearing loss produced is not directly proportional to the noise intensity or exposure time, but also influences individual susceptibility. This issue has been best seen in the proffesional deafness of noise exposure for workers in a company, where they are often subjected to the same noise the same hours a day, and not all are affected in the same way.
- What can be done to reduce the risk of hearing loss in young people? What do you advise to prevent hearing loss?
 |
| Teresa Rivera |
Neurosensory hearing loss caused by noise is irreversible, and does not have a curative treatment that restores hearing at present. The only way to treat this deafness is through electronic devices, hearing aids or hearing implants. In these cases, the patient is still deaf, but has a device that allows him to hear the sounds and understand the words, allowing him to be able to relate properly.
Therefore, prevention is the best way to act, avoiding exposure to intense noise. In the case of noise at work, the worker must be protected by means of helmets or headphones. In these cases, the company is obliged to provide the worker with adequate protection.
This translation has been created by uah.esnoticia magazine.
Publicado en: Inglés